README.md 9.0 KB
Mol* MolViewSpec extension
MolViewSpec (MVS) is a tool for standardized description of reproducible molecular visualizations shareable across software applications.
MolViewSpec provides a generic description of typical visual scenes that may occur as part of molecular visualizations. A tree format allows the composition of complex scene descriptors by combining reoccurring nodes that serve as building blocks.
More sources:
- MolViewSpec home page: https://molstar.org/mol-view-spec/
- Python library
molviewspecfor building MolViewSpec views: https://pypi.org/project/molviewspec/ - Python library
molviewspecin action: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1O2TldXlS01s-YgkD9gy87vWsfCBTYuz9
MolViewSpec data structure
MVS is based on a tree format, i.e. a molecular view is described as a tree where individual node types represent common data operations needed to create the view (e.g. download, parse, color). Each node can have parameters that provide additional details for the operation.
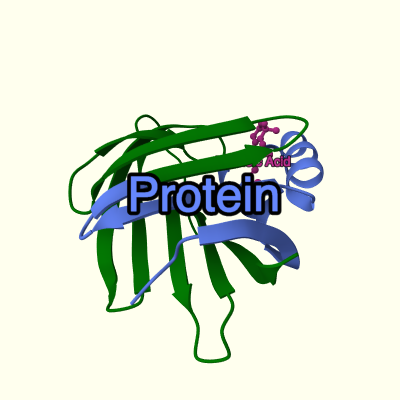
A simple example of a MVS tree showing PDB structure 1cbs:
- root {}
- download {url: "https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/entry-files/1cbs.bcif"}
- parse {format: "bcif"}
- structure {type: "model"}
- component {selector: "polymer"}
- representation {type: "cartoon"}
- color {color: "green"}
- color {selector: {label_asym_id: "A", beg_label_seq_id: 1, end_label_seq_id: 50}, color: "#6688ff"}
- label {text: "Protein"}
- component {selector: "ligand"}
- representation {type: "ball_and_stick"}
- color {color: "#cc3399"}
- label {text: "Retinoic Acid"}
- canvas {background_color: "#ffffee"}
- camera {target: [17,21,27], position: [41,34,69], up: [-0.129,0.966,-0.224]}
(This is just a human-friendly representation of the tree, not the actual data format!)
A complete list of supported node types and their parameters is described by the MVS tree schema.
Encoding
A MolViewSpec tree can be encoded and stored in .mvsj format, which is basically a JSON representation of the tree with additional metadata:
{
"metadata": {
"title": "Example MolViewSpec - 1cbs with labelled protein and ligand",
"version": "1",
"timestamp": "2023-11-24T10:38:17.483Z"
},
"root": {
"kind": "root",
"children": [
{
"kind": "download",
"params": {"url": "https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/entry-files/1cbs.bcif"},
"children": [
{
"kind": "parse",
"params": {"format": "bcif"},
"children": [
...
Complete file: 1cbs.mvsj
MolViewSpec extension functionality
Mol* MolViewSpec extension provides functionality for building, validating, and visualizing MVS views.
Graphical user interface
Drag&drop support: The easiest way to load a MVS view into Mol* Viewer is to drag a
.mvsjfile and drop it in a browser window with Mol* Viewer.Load via menu: Another way to load a MVS view is to use "Download File" or "Open Files" action, available in the "Home" tab in the left panel. For these actions, the "Format" parameter must be set to "MVSJ" (in the "Miscellaneous" category) or "Auto".
URL parameters: Mol* Viewer supports
mvs-url,mvs-data, andmvs-formatURL parameters to specify a MVS view to be loaded when the viewer is initialized.mvs-urlspecifies the address from which the MVS view should be retrieved.mvs-dataspecifies the MVS view data directly. Keep in mind that some characters must be escaped to be used in the URL. Also beware that URLs longer than 2000 character may not work in all browsers.mvs-formatspecifies the format of the MVS view data (frommvs-urlormvs-data). The only allowed (and default) value ismvsj, as this is currently the only supported format.
Examples of URL parameter usage:
Programming interface
Most functions for manipulation of MVS data (including parsing, encoding, validating, and building) are provided by the MVSData object (defined in src/extensions/mvs/mvs-data.ts). In TypeScript, MVSData is also the type for a MVS view.
The loadMVS function (defined in src/extensions/mvs/load.ts) can be used to load MVS view data into Mol* Viewer.
Example usage:
// Fetch a MVS, validate, and load
const response = await fetch('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/molstar/molstar/master/examples/mvs/1cbs.mvsj');
const rawData = await response.text();
const mvsData: MVSData = MVSData.fromMVSJ(rawData);
if (!MVSData.isValid(mvsData)) throw new Error(`Oh no: ${MVSData.validationIssues(mvsData)}`);
await loadMVS(this.plugin, mvsData, { replaceExisting: true });
console.log('Loaded this:', MVSData.toPrettyString(mvsData));
console.log('Loaded this:', MVSData.toMVSJ(mvsData));
// Build a MVS and load
const builder = MVSData.createBuilder();
const structure = builder
.download({ url: 'https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/entry-files/download/1og2_updated.cif' })
.parse({ format: 'mmcif' })
.modelStructure();
structure
.component({ selector: 'polymer' })
.representation({ type: 'cartoon' });
structure
.component({ selector: 'ligand' })
.representation({ type: 'ball_and_stick' })
.color({ color: '#aa55ff' });
const mvsData2: MVSData = builder.getState();
await loadMVS(this.plugin, mvsData2, { replaceExisting: false });
When using the pre-built Mol* plugin bundle, MVSData and loadMVS are exposed as molstar.PluginExtensions.mvs.MVSData and molstar.PluginExtensions.mvs.loadMVS. Furthermore, the molstar.Viewer class has loadMvsFromUrl and loadMvsData methods, providing the same functionality as mvs-url and mvs-data URL parameters.
Command-line utilities
The MVS extension in Mol* provides a few command-line utilities, which can be executed via NodeJS:
mvs-validateprovides validation of MolViewSpec filesmvs-rendercreates images based on MolViewSpec filesmvs-print-schemaprints MolViewSpec tree schema (i.e. currently supported node types and their parameters)
Example usage:
# Validate a MolViewSpec file `examples/mvs/1cbs.mvsj`
node lib/commonjs/cli/mvs/mvs-validate examples/mvs/1cbs.mvsj
# Render a MolViewSpec file `examples/mvs/1cbs.mvsj` to `../outputs/1cbs.png`
npm install --no-save canvas gl jpeg-js pngjs # Might be needed before the first execution
node lib/commonjs/cli/mvs/mvs-render -i examples/mvs/1cbs.mvsj -o ../outputs/1cbs.png --size 800x600 --molj
# Print MolViewSpec tree schema formatted as markdown
node lib/commonjs/cli/mvs/mvs-print-schema --markdown
(If you installed Mol* package from the npm repository, use can just type npx mvs-validate...).